Conceptual Overview - OpenADR and Canvas
This section provides a basic overview of how OpenADR works, how Canvas implements it, different options for implementing Canvas. For more discussion and information, see our various information on the topics covered in our blog.
OpenADR
OpenADR is a protocol built to facilitate demand response and load shifting communication on the power grid. It is a server/client protocol, meant to facilitate communications between one central hub and many nodes. The simplest way to conceptualize the model is that the server side represents utilities and the client side represents end device owners or operators. Examples of end devices could be:
- Thermostats
- Water Heaters
- EV Chargers
- Solar / Storage / Inverters
- Building Management Systems
- Lighting Controls Systems
- Industrial Controls Systems
OpenADR defines the communication between the utility and the end devices. Within OpenADR, the nomenclature for the server side is Virtual Top Nodes, or VTN, and Virtual End Node, or VEN, for the client side. VTNs and VENs are connected in a one to many relationship.
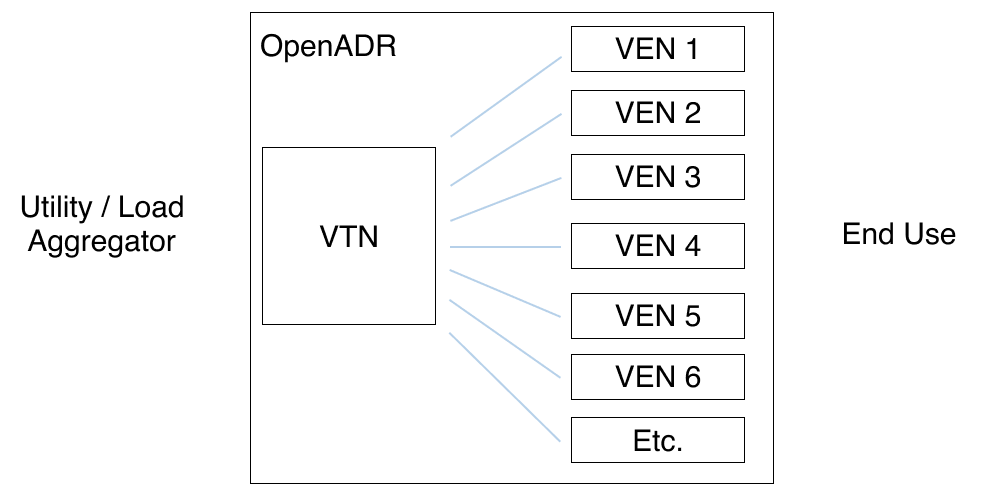
The above diagram shows very simply how OpenADR is set up and connects to end devices. While that implementation does happen, especially in pilot programs, larger scale load shifting programs usually have a lot more going on. The following diagram gives a better indication of how it typically fits within a DERMS (distributed energy resource management system) or DRMS (demand response management system), which would in turn administer a load shifting or demand response program.
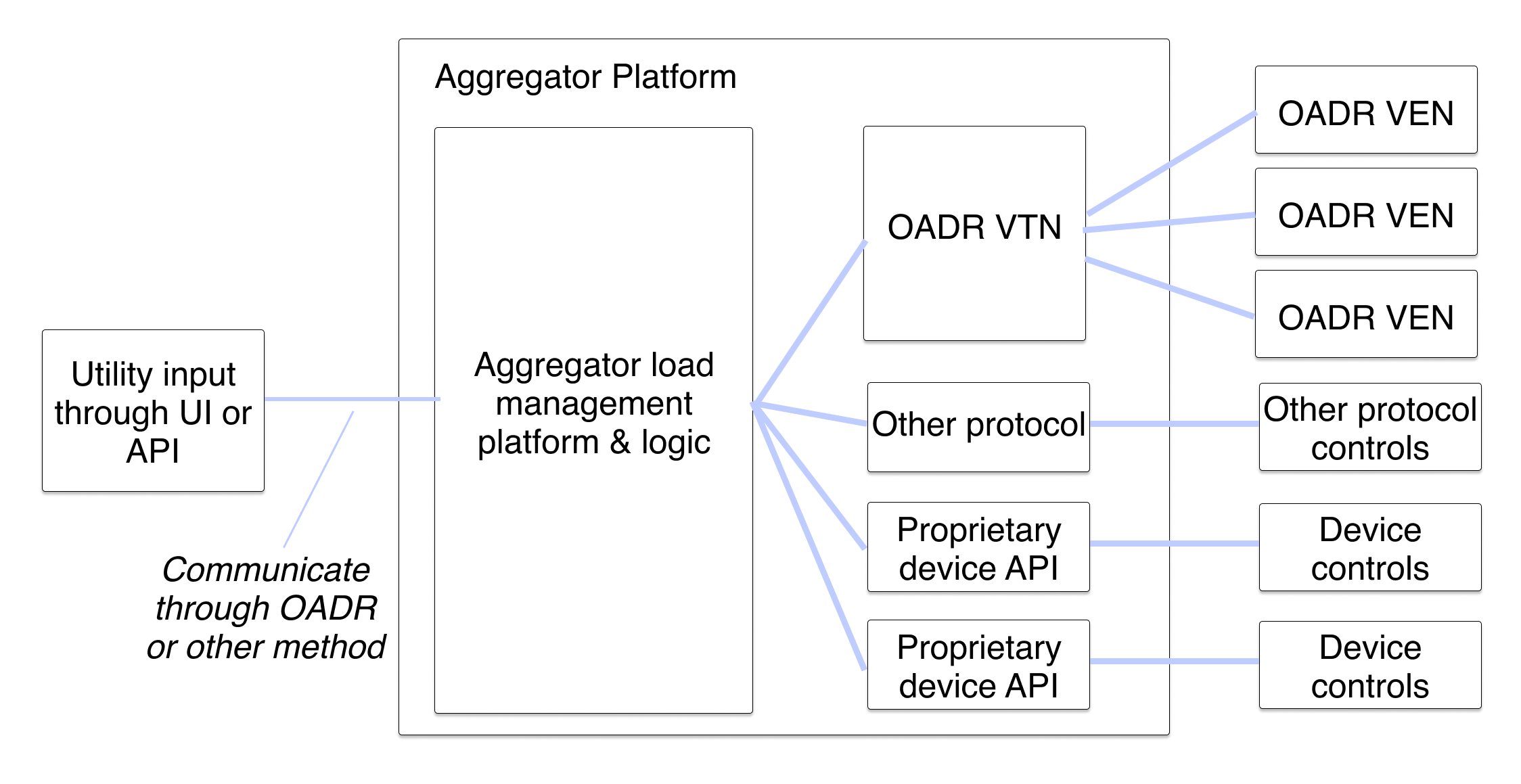
Why OpenADR
OpenADR solves the problem of normalization. If every utility and implementer had to integrate individually with every device company, that would lead to a lot of wasted work and expensive integrations. By providing a universal standard, it is easier for devices and load shifting programs to integrate together.
4 things that OpenADR normalizes communications for are:
- Events: VTN communicates information about upcoming load shifting requirements and market conditions
- Registration: registers a VEN to a VTN, (for security, this also requires a step outside of OpenADR to communicate the secure certificate fingerprint)
- Opts: VEN communicates whether it will be participating in a given event
- Reports: VEN communicates reporting
OpenADR also well defines the problem of which party is responsible for what. It describes market conditions (e.g. there is an event on Tuesday between 4-6pm), but does not have specific commands for controlling devices (e.g. telling thermostats to increase set points). Think, inform and motivate, rather than command and control.
The general philosophy behind this is that devices manufacturers or owners should know best how their devices should operate in different conditions and therefore should be the ones making those decisions. All they need from utilities is information about market conditions so that they may respond appropriately. This means that the ultimate responsibility for end device controls falls to the device owner or controller, which generally leads to cleaner outcomes for the utility and DR aggregators.
Canvas Implementation
Canvas is an OpenADR VTN. It fully implements OpenADR 2.0b and is used to connect to and communicate with OpenADR VENs.
We offer Canvas in two different implementations, each with a specific use case.
Canvas Cloud, for testing & piloting
Use Case
It is meant to be used either for utilities or aggregators to pilot load shifting programs, or by VEN developers to test out their VEN functionality by giving them a VTN they can connect to and send messages from. Using the reference from above, it is meant to be used in the scenario described in the first, "Simple" representation of OpenADR.
Delivery Model
Canvas Cloud is a SaaS solution, hosted by GridFabric. It requires no IT overhead and is billed monthly with no up-front investment required. While we make every effort to maintain service, we do not guarantee uptime for Canvas Cloud.
Interface
Canvas Cloud is controlled via a web app. All OpenADR functionality is available and controlled through a UI. Canvas Cloud does not offer the ability to control the VTN through an API.
Canvas Server, for self hosting and production load shifting
Use Case
Canvas Server is a licensed software VTN. Therefore it is hosted by our customers, and that means it can scale to large OpenADR implementations, be embedded into DERMS and DRMS systems, or extended for research programs.
Delivery model
Canvas Server is a licensed software solution, hosted by the customer. It is embedded in a customer's existing server or cloud platform and run entirely in their ecosystem. This means it can scale as much as the customer needs it to, and customers can guarantee uptime.
Interface
Customer's systems communicate with it through an API, and it acts as the translation layer between their existing device controls logic and OpenADR.
Summary
OpenADR is an important part of demand response and load shifting in North America and increasingly worldwide. An OpenADR VTN is required to communicate to OpenADR end nodes. Canvas is offered as either a SaaS solution for piloting and testing purposes, or as a hosted solution for use at scale or as a part of a DRMS / DERMS.
If you have any questions or clarifications on these topics, please look through the FAQs or feel free to reach out through support@gridfabric.zendesk.com.